SSH keys are a way to identify trusted computers, without involving passwords. The steps below will walk you through generating an SSH key and adding the public key to the server.
SSH keys are created using a key generation tool. The SSH command line tool suite includes a keygen tool. Most git hosting providers offer guides on how to create an SSH Key. Generate an SSH Key on Mac and Linux. Both OsX and Linux operating systems have comprehensive modern terminal applications that ship with the SSH suite installed. Jul 20, 2019 No mention of using a ssh agent (putty pageant on windows) to manage keys. No mention of the benefits of using a smart card (or yubikey) to store and protect your private key further. Simply setting your name and email in your git config doesn't sign your commits, you need gpg for that, again a smart card is the way forward.
If you are using another terminal prompt, such as Git for Windows, you can use the 'Auto-launching the ssh-agent' instructions in 'Working with SSH key passphrases', or start it manually: # start the ssh-agent in the background $ eval $(ssh-agent -s) Agent pid 59566; Add your SSH private key to the ssh-agent. You can generate a new SSH key for authentication using the following command in Git Bash − $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C 'youremail@mail.com' If you already have a SSH key, then don't a generate new key, as they will be overwritten. You can use ssh-keygen command, only if you have installed Git with Git Bash. When you run the above command, it will create 2 files in the /.ssh directory. /.ssh/idrsa − It is. Idrsa.pub: this is the public key of your SSH key pair, this is the key that you will copy to your server in order to connect to it seamlessly. Generate SSH keys for Git on Windows In order to generate SSH keys for Git on Windows, you have to enable the OpenSSH commands using the “Add-WindowsCapability” command. Generating Your SSH Public Key That being said, many Git servers authenticate using SSH public keys. In order to provide a public key, each user in your system must generate one if they don’t already have one.
Step 1: Check for SSH Keys
First, check for existing SSH keys on your computer. Open Git Bash, Cygwin, or Terminal, etc. and enter:
Check the directory listing to see if you already have a public SSH key. By default, the filenames of the public keys are one of the following:
- id_dsa.pub
- is_ecdsa.pub
- id_ed25519.pub
- id_rsa.pub
If you see an existing public and private key pair listed (for example id_rsa.pub and id_rsa) that you’d like to use, you can skip Step 2 and go straight to Step 3.
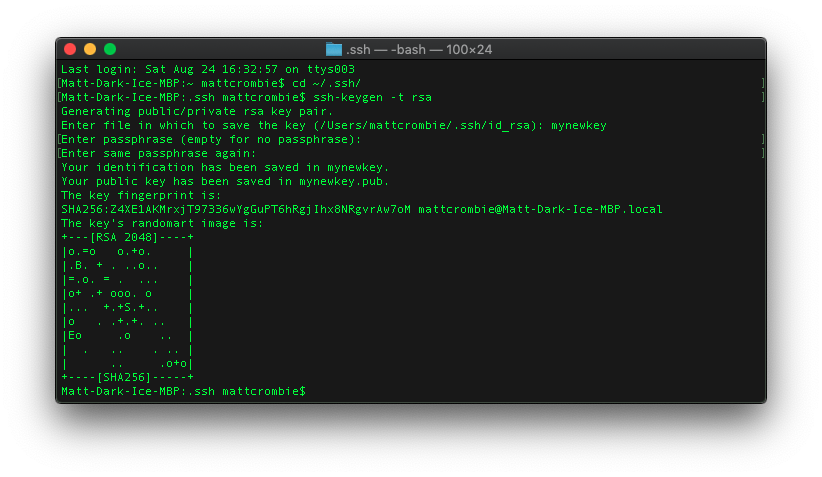
Step 2: Generate a new SSH key
With your command line tool still open, enter the text shown below. Make sure you substitute in your email address:
You’ll be asked to enter a passphrase, or simply press Enter to not enter a passphrase:
After you enter a passphrase (or just press Enter twice), review the fingerprint, or ‘id’ of your SSH key:
Step 3: Add your key to the ssh-agent
To configure the ssh-agent program to use your SSH key, first ensure ssh-agent is enabled.
If you are using Git Bash, turn on the ssh-agent with command shown below instead:
Then, add your SSH key to the ssh-agent:
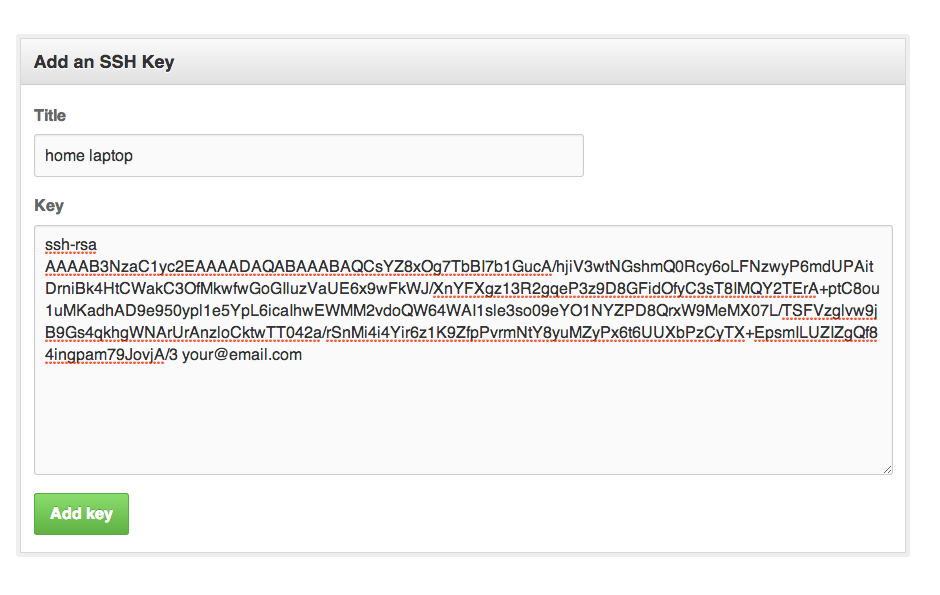
Step 4: Add your SSH key to the server
To add your public SSH key to the server, you’ll copy the public SSH key you just created to the server. Substitute “username” with your username on the server, and “server.address.com” with the domain address or IP address of your server:
Puttygen
The server will then prompt you for your password:
Ssh Key Generation Using Git File
That’s it! You should now be set up to connect to the server without having to authenticate.