- How Are Private And Public Keys Generated Home
- Generate Key File With Keygen
- Public Key Example
- How Are Private And Public Keys Generated Money
- How Are Public And Private Keys Generated
- Create Public Key
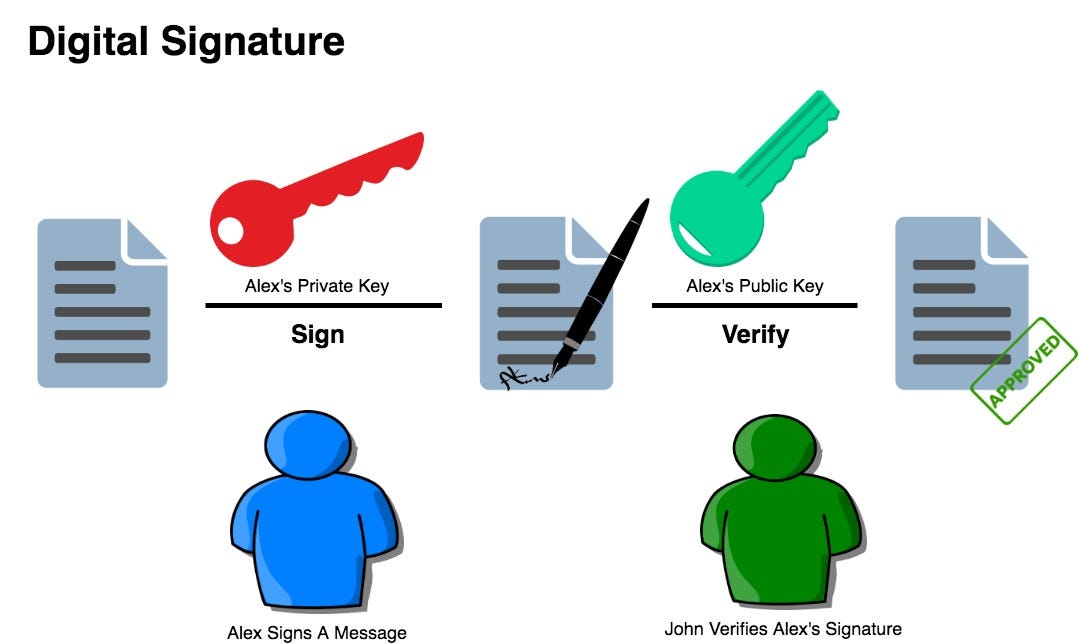
Asymmetric keys can be either stored for use in multiple sessions or generated for one session only. While the public key can be made generally available, the private key should be closely guarded. A public/private key pair is generated whenever a new instance of an asymmetric algorithm class is created. Public Key Cryptography, or Asymmetric Cryptography, is a cryptographic system that uses pairs of keys: Public Key and Private Key. It is one of the most important (if not the most important) part of cryptocurrency protocols, and it is used in sev. A SSH private key as generated by ssh-keygen contains a public key part. How do I retrieve this public key from the private key? I've lost my public key and need to put the contents of this public key in the servers authorizedkeys file and do not want to create a new key pair. Alternatively phrased: how do I create the idrsa.pub file from a. Oct 18, 2016 The encryption keys generated in modern cryptographic algorithms are generated depending upon the algorithm used. Primarily there are two types of encryption schemes: Symmetric and Asymmetric(Public Key encryption). Symmetric Encryption schemes li. Once keys are generated, we can use ToXmlString or ExportParameters method to read the keys. The ToXmlString method returns key information in XML as a string. The method takes a Boolean parameter. If passed false, it returns public key only. If passed true, it returns both private and public pair. The following code snippet returns a public key.
If you interact regularly with SSH commands and remote hosts, you may find that using a key pair instead of passwords can be convenient. Instead of the remote system prompting for a password with each connection, authentication can be automatically negotiated using a public and private key pair.
The private key remains secure on your own workstation, and the public key gets placed in a specific location on each remote system that you access. Your private key may be secured locally with a passphrase. A local caching program such as ssh-agent or gnome-keyring allows you to enter that passphrase periodically, instead of each time you use the key to access a remote system.
Generating a key pair and propagating the public key
Generating your key pair and propagating your public key is simpler than it sounds. Let’s walk through it.
Generating the key
The minimum effort to generate a key pair involves running the ssh-keygen command, and choosing the defaults at all the prompts:
The default location to store the keys is in the ~/.ssh directory, which will be created if it does not exist:
Allowing this command to create the directory also ensures that the owner and permissions are set correctly. Some applications will not use keys if the permissions to the private key are too open.
The file ending in .pub is the public key that needs to be transferred to the remote systems. It is a file containing a single line: The protocol, the key, and an email used as an identifier. Options for the ssh-keygen command allow you to specify a different identifier:
After generating the key pair, the ssh-keygen command also displays the fingerprint and randomart image that are unique to this key. This information can be shared with other people who may need to verify your public key.
Later you can view these with:
The -l option lists the fingerprint, and the -v option adds the ASCII art.
Propagating the public key to a remote system
If password authentication is currently enabled, then the easiest way to transfer the public key to the remote host is with the ssh-copy-id command. If you used the default name for the key all you need to specify is the remote user and host:
Following the instructions from the output, verify that you can connect using the key pair. If you implemented a passphrase, you will be prompted for the passphrase to use the private key:
Examine the resulting authorized key file. This is where the public key was appended. If the directory or file did not exist, then it was (or they were) created with the correct ownership and permissions. Each line is a single authorized public key:
To revoke access for this key pair, remove the line for the public key.
There are many other options that can be added to this line in the authorized key file to control access. These options are usually used by administrators placing the public keys on a system with restrictions. These restrictions may include where the connection may originate, what command(s) may be run, and even a date indicating when to stop accepting this key. These and more options are listed in the sshd man page.
Changing the passphrase
If you need to change a passphrase on your private key or if you initially set an empty passphrase and want that protection at a later time, use the ssh-keygen command with the -p option:
You can add additional options to specify the key (-f), and the old (-P) or new (-N) passphrases on the command line. Remember that any passwords specified on the command line will be saved in your shell history.
See the ssh-keygen man page for additional options.
Rotating keys
While the public key by itself is meant to be shared, keep in mind that if someone obtains your private key, they can then use that to access all systems that have the public key. These key pairs also do not have a period of validity like GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) keys or public key infrastructure (PKI) certificates.
If you have any reason to suspect that a private key has been stolen or otherwise compromised, you should replace that key pair. The old public key has to be removed from all systems, a new key has to be generated with ssh-keygen, and the new public key has to be transferred to the desired remote systems.
If you are rotating keys as a precaution and without any concern of compromise, you can use the old key pair to authenticate the transfer of the new public key before removing the old key.

Is using empty passphrases ever a good idea?
There are several things to think about when considering an empty passphrase for your SSH private key.
How secure is the private key file?
If you tend to work from multiple client systems and want to either have multiple copies of your key or keep a copy on removable media, then it really is a good idea to have a passphrase on the private key. This practice is in addition to protecting access to the key file with encrypted media.
However, if you have only one copy of the private key and it is kept on a system that is well secured and not shared, then having a passphrase is simply one more level of protection just in case.
Remember that changing the passphrase on one copy does not change the passphrase on other copies. The passphrase is simply locking access to a specific key file.
Why do think you need an empty passphrase?
There are cases for keys with empty passphrases. Some utilities that need to automatically transfer files between systems need a passwordless method to authenticate. The kdump utility, when configured to dump the kernel to a remote system using SSH, is one example.
Another common use is to generate a key pair for a script that is designed to run unattended, such as from a cron job.
How about a middle ground alternative?
By itself, a passphrase-protected private key requires the passphrase to be entered each time the key is used. This setup does not feel like passwordless SSH. However, there are caching mechanisms that allow you to enter the key passphrase once and then use the key over and over without reentering that passphrase.
More Linux resources
OpenSSH comes with an ssh-agent daemon and an ssh-add utility to cache the unlocked private key. The GNOME desktop also has a keyring daemon that stores passwords and secrets but also implements an SSH agent.
The lifetime of the cached key can be configured with each of the agents or when the key is added. In many cases, it defaults to an unlimited lifetime, but the cache is cleared when the user logs out of the system. You will be prompted for the passphrase only once per login session.
If there is a scheduled application that needs to run outside of a user login session, it may be possible to use a secret or other password manager to automate the unlocking of the key. For example, Ansible Tower stores credentials in a secure database. This database includes an SSH private key used to connect to the remote systems (managed nodes), and any passphrases necessary for those private keys. Once those credentials are stored, a job can be scheduled to run a playbook on a regular schedule.
Automating propagation
A centralized identity manager such as FreeIPA can assist with key propagation. Upload the public key to the server as an attribute of a user account, and then propagate it to the hosts in the domain as needed. FreeIPA can also provide additional host-based access control for where a key may be used.
Keys can also be distributed using Ansible modules. The openssh_keypair module uses ssh-keygen to generate keys and the authorized_key module adds and removes SSH authorized keys for particular user accounts.
Wrapping up
SSH key pairs are only one way to automate authentication without passwords. Using the Generic Security Services Application Program Interface (GSSAPI) authentication is also common when trying to reduce the use of passwords on a network with centralized user management. SSH key pairs are the easier option to implement when single sign-on (SSO) is not already available.
Many source code repositories grant access using SSH keys. You can upload a public key to an account in the hosting organization such as the Fedora Account System, GitLab, or GitHub sites and use that key pair to authenticate when pulling and pushing content to repositories.
Free Event: Red Hat Summit 2020 Virtual Experience
Attend the Red Hat Summit 2020 virtual experience, April 28-29.
Related Content
-->Creating and managing keys is an important part of the cryptographic process. Symmetric algorithms require the creation of a key and an initialization vector (IV). The key must be kept secret from anyone who should not decrypt your data. The IV does not have to be secret, but should be changed for each session. Asymmetric algorithms require the creation of a public key and a private key. The public key can be made public to anyone, while the private key must known only by the party who will decrypt the data encrypted with the public key. This section describes how to generate and manage keys for both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms.
Symmetric Keys
How Are Private And Public Keys Generated Home
The symmetric encryption classes supplied by the .NET Framework require a key and a new initialization vector (IV) to encrypt and decrypt data. Whenever you create a new instance of one of the managed symmetric cryptographic classes using the parameterless constructor, a new key and IV are automatically created. Anyone that you allow to decrypt your data must possess the same key and IV and use the same algorithm. Generally, a new key and IV should be created for every session, and neither the key nor IV should be stored for use in a later session.
Generate Key File With Keygen
To communicate a symmetric key and IV to a remote party, you would usually encrypt the symmetric key by using asymmetric encryption. Sending the key across an insecure network without encrypting it is unsafe, because anyone who intercepts the key and IV can then decrypt your data. For more information about exchanging data by using encryption, see Creating a Cryptographic Scheme.
The following example shows the creation of a new instance of the TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider class that implements the TripleDES algorithm.
Public Key Example
When the previous code is executed, a new key and IV are generated and placed in the Key and IV properties, respectively.
Sometimes you might need to generate multiple keys. In this situation, you can create a new instance of a class that implements a symmetric algorithm and then create a new key and IV by calling the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods. The following code example illustrates how to create new keys and IVs after a new instance of the symmetric cryptographic class has been made.
When the previous code is executed, a key and IV are generated when the new instance of TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider/windows-8-oem-key-generator.html. is made. Another key and IV are created when the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods are called.
Asymmetric Keys
The .NET Framework provides the RSACryptoServiceProvider and DSACryptoServiceProvider classes for asymmetric encryption. These classes create a public/private key pair when you use the parameterless constructor to create a new instance. Asymmetric keys can be either stored for use in multiple sessions or generated for one session only. While the public key can be made generally available, the private key should be closely guarded.
A public/private key pair is generated whenever a new instance of an asymmetric algorithm class is created. After a new instance of the class is created, the key information can be extracted using one of two methods:
The ToXmlString method, which returns an XML representation of the key information.
The ExportParameters method, which returns an RSAParameters structure that holds the key information.
Both methods accept a Boolean value that indicates whether to return only the public key information or to return both the public-key and the private-key information. An RSACryptoServiceProvider class can be initialized to the value of an RSAParameters structure by using the ImportParameters method.
How Are Private And Public Keys Generated Money
Asymmetric private keys should never be stored verbatim or in plain text on the local computer. If you need to store a private key, you should use a key container. For more on how to store a private key in a key container, see How to: Store Asymmetric Keys in a Key Container.
How Are Public And Private Keys Generated
The following code example creates a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class, creating a public/private key pair, and saves the public key information to an RSAParameters structure.